The Google Search Console is the greatest gift by Google for all SEO experts and SEO enthusiasts who want to improve the site’s appearance on SERPs. Best of all, you don’t need to know about HTML or coding since all data is understandable for people who understand the technology. However, you need to know how the website is organized and written and ready to employ changes according to the Console’s gathered insights. Basically, this text is for all of you interested in optimizing your website for the search engines and designing, planning, and executing the on-page and off-page SEO strategy for a website. Let’s cover all the aspects you should know in this Google Search Console Tutorial.
Table of Contents
What is Google Search Console?

To begin with, let’s get familiar with the tool. Google offers the Search console for free to help you monitor, maintain, and find problems with the website’s presence online. There is no need to sign up to ensure that your site will appear on SERP. Instead, you need to use this free service so you can understand how Google sees your site and use that knowledge to improve its rankings.
Here is what Google Search Console can perform:
- Confirm that Google sees your site and is able to crawl it.
- Find and fix indexing problems and ask for re-indexing of the new or updated content.
- Give precise data about the Google Search traffic data for your site.
- Receive alerts when Google finds problems with indexing or spam.
- See the backlinks to your site.
- Troubleshoot issues for AMP, mobile usability, and other search features.
Who Will Benefit the Most from Using Google Search Console?
As mentioned above, SEO experts will find the Console of extreme usefulness. However, other people involved in the maintenance of the site can enjoy its benefits as well. For example, business owners should be aware of the features and how they can help them run their business website better; the site administrators can monitor the site’s performance and troubleshoot any errors and site load issues. In addition, they can prevent the site from being attacked by hackers or malware. Finally, the web developers can use the Search Console’s features to create or resolve any issues with markup/structured data.
How to Start Using the Google Search Console?
There are several steps to get started. Here they are.
1. Signing up
You need to sign up to start using it. It is entirely free, and there are no upgrades or paid features. You go to the welcome page of the Google Search Console, and you sign up by using the Domain or by the URL prefix.
If you choose the Domain, the Console will gather data from all URLs across all subdomains, all URLs across HTTPS or HTTP. It requires DNS verification.
If you decide to sign up with the URL prefix, the GSC will gather data only from URLs under entered address and only from URLs under the specified protocol. It allows multiple verification methods.
2. Verification
Of course, you will need to prove that you are the site owner because Google will show sensitive data, and only the site’s owner should know. You can verify immediately by following the verification steps without closing the popup window. As it takes some time, you can always save the settings and proceed later. Once the account is verified, Google will start showing data in your Google Search Console account a few days, even from the non-verified period.
The verification methods are:
- HTML file upload
- HTML tag
- Domain name provider
- Google Analytics tracking code
- Tag Manager container snippet
- Google SItes
- Blogger
- Google Domains
3. Read Google’s Guides and Start Exploring
Google has prepared extensive guides for using the Google Search Console, so you can always go straight to the source and start learning if you have time. However, it might be too overwhelming to jump in the pool with so much information at once. Therefore, you can aim for a simple but vital info type of Google Search Console Tutorial, like the one you are reading right now.
Understanding the Basics of Google Search Console
Overview Report
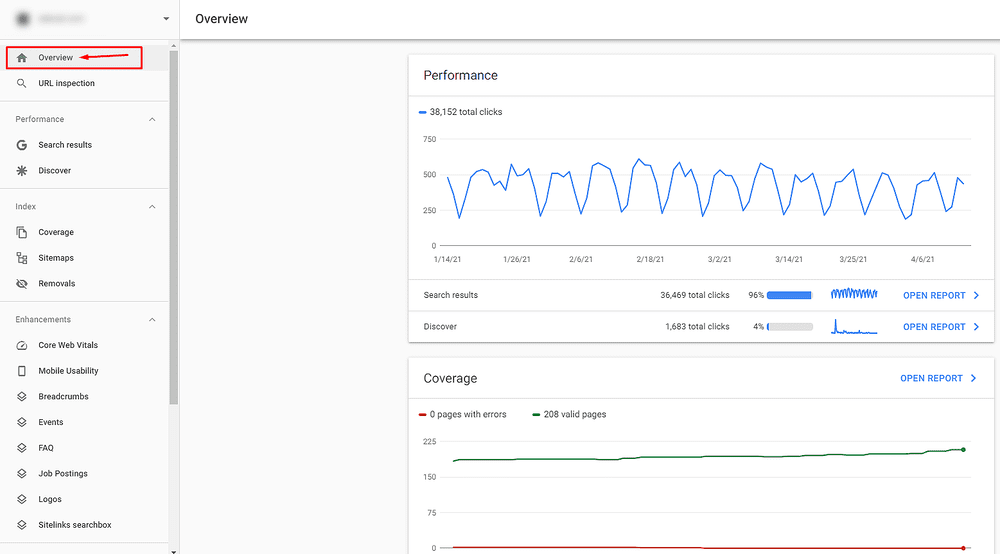
When you open the Search Console, first, you get to see the Overview Report. It consists of three main reports: Performance, Coverage, and Enhancements.
- The Performance overview section shows the number of total clicks over the days
- The Coverage section shows how many pages are valid and how many with errors
- The Enhancement section shows whether your structured data is working and whether your AMP pages are active.
Each of these sections can be opened separately. The data inside is categorized clearly, and you can explore it by using various filters to get the exact insights you need. (Look below at the explanations)
URL Inspection
Next, below the Overview report is the URL Inspection. This section tells you how Google views your website. Moreover, you can test how Google renders your site. Also, you can use this tool to submit the URL of your new blog post or a redesigned webpage to tell Google that it needs to crawl that page.
All you need to do is enter the URL of the page you want to get info about whether the URL is indexed when it was last crawled and what kind of enhancements it has (mobile usability, breadcrumbs, FAQ, Logos, sitelinks search box)
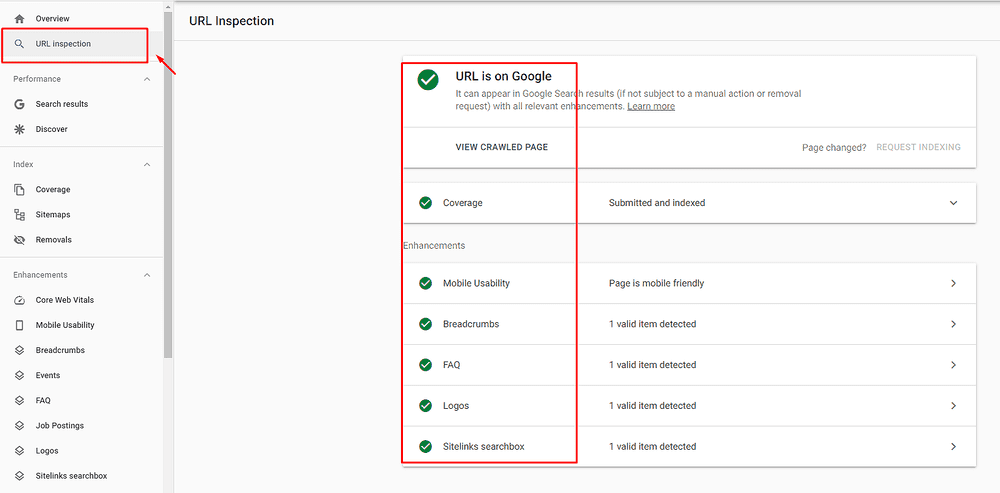
Other activities you can perform with the URL Inspection tool are:
- Update an old webpage
- Launch a new section of your website
- Introduce a new mobile design
- Update robots.txt file
- Implement rel=canonical tags
- Transit from HTTP to HTTPS
Performance
Now, let’s take a closer look at the Performance section and what kind of data you can get from here. It is subcategorized into Search Results and Discover.
Search Results Report in GSC
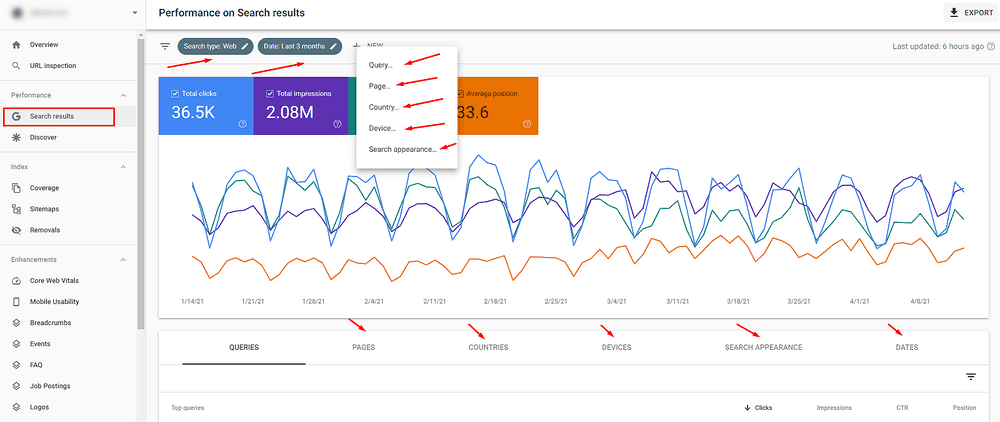
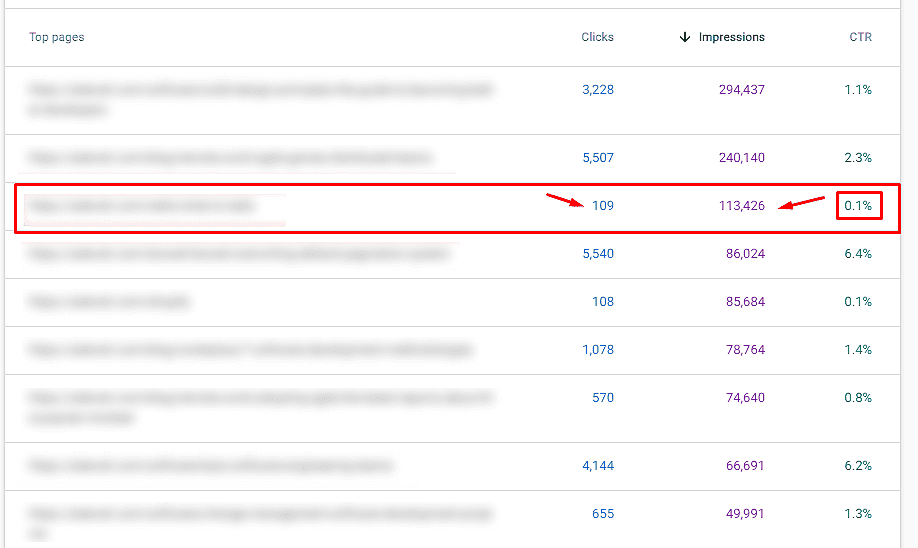
As you can see from the screenshot above, you can see the total number of clicks, impressions, average CTR, and average position of the organic queries or pages. You can filter the results. Also, you can see from which countries the organic traffic come from, from what type of devices (desktop, mobile, tablet), how the results appear in the SERP (FAQ rich results, Videos, Rich results, Web Light results, etc.), and you can also choose the particular dates for the analysis.
By using the data from this section, you can identify your top-performing pages, the pages with the highest/lowest CTR, the number of clicks per keyword, and the number of clicks per keyword.
How will this be of use to you?
Let’s take a practical example – if the page has lots of impressions but a low number of clicks, that might indicate that your Meta description and Title tag are not optimized with the relevant keywords (The webpage is shown in SERP a lot of the times for the specific keyword, but searchers don’t click on it because it doesn’t seem attractive). To ensure you have the most attractive results in the SERPs, you need to focus on this part of your SEO strategy and use GSC data to fix the issues.
Discover Report in GSC
This is a relatively new addition to the menu (from April 2019, to be exact) and helps you understand how searchers discover your website content.
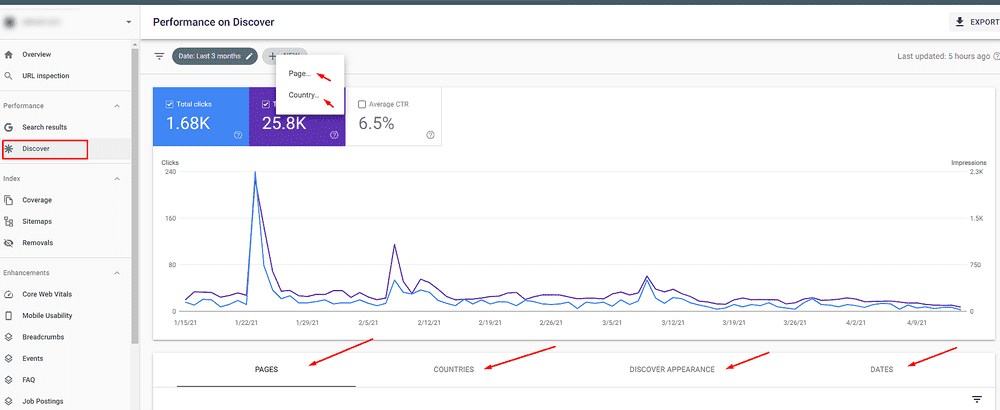
With this report’s insights, you can see how searchers interact with your site, both on Google’s mobile Discover feed and Chrome mobile browser. It includes the best-performing pages, how your content is performing compared to other traditional search results, and how often the searchers are visiting your site.
Index
Let’s have a look at the Index section in this Search Console tutorial. There are three categories: Coverage, SItemaps, and Removals. You will use this section when you want to check whether the pages are indexed, whether your CSS is blocked, or if you want to remove URLs. Here is how.
Coverage Report
This report displays the indexed pages and the pages that are not included in the sitemap. You will see a list of errors and broken pages, as well. To check whether all your indexed pages are receiving traffic, you need to compare the number of pages from the Coverage report to the number of landing pages that receive organic traffic in Google Analytics. The numbers should match; if not, that means that a small fraction of the indexed pages is visited by searchers.
Here, you can also put a noindex tag to each page that you don’t want to be indexed. Once you do that, you need to disallow them in the robots.txt file.
Sitemaps Report
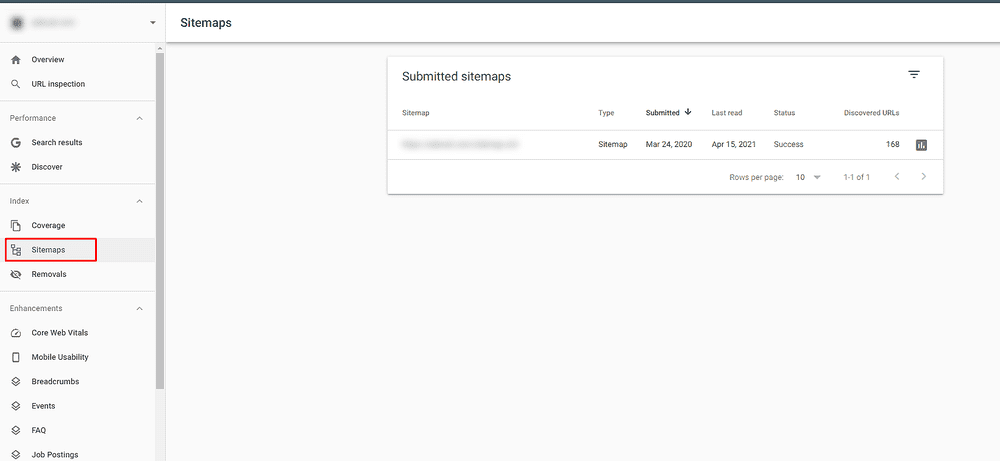
The sitemap report tells you all you need to know about your website sitemaps. If there are any errors, you should fix them as soon as possible. Sometimes, the error might be very tiny but causing a lot of damage, such as preventing the pages from being indexed.
Removals
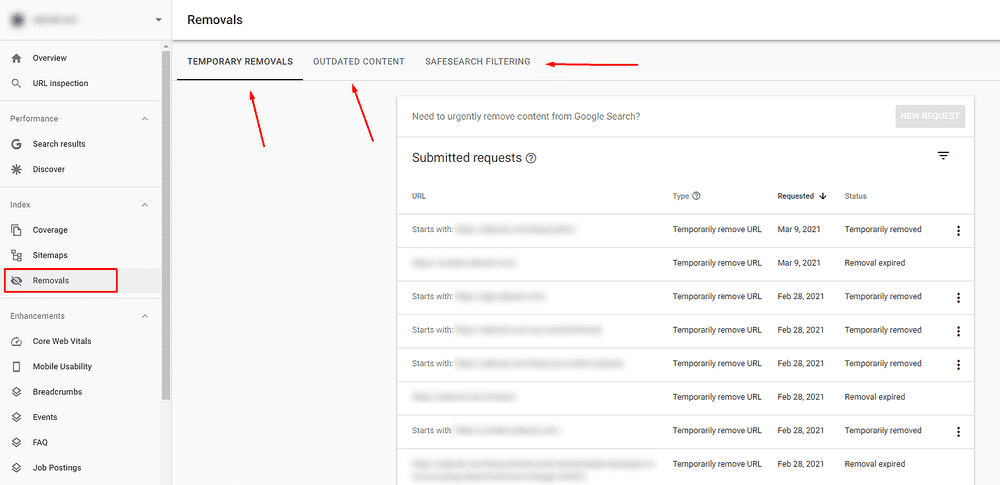
With this report, thin or duplicate content can be detected. For that purpose, there are three categories in the Removals section: Temporary Removals, Outdated Content, SafeSearch Filtering. Here are their uses.
Temporary Removals
You use this section to temporarily hide something from Google searches by adding the URL of the page you want to hide. You’d want to hide pages with thin content or duplicate content so you can avoid Google search bots crawling these pages. Once you enter the URL in the temporary removal – the page will be hidden for six months, while it takes a day to process the newly put info. However, you should consider blocking the URL in the robots.txt or do a 404 at some point over this period.
Outdated Content
Here you can see the removal requests sent by the public. This means that any person that views the page can suggest an update to your search results if there is no correct information about the page available. The data that you can view is from the past six months.
SafeSearch Filtering
In the final category, all content that is reported as adult content using the SafeSearch suggestion tool will be listed here.
Enhancements
This is the section that SEO experts dwell in a lot. In the Enhancement section, you can reveal all the secrets about the structured data and check whether your AMP pages are active. There are eight reports here, and here is what you should know about them.
Core Web Vitals
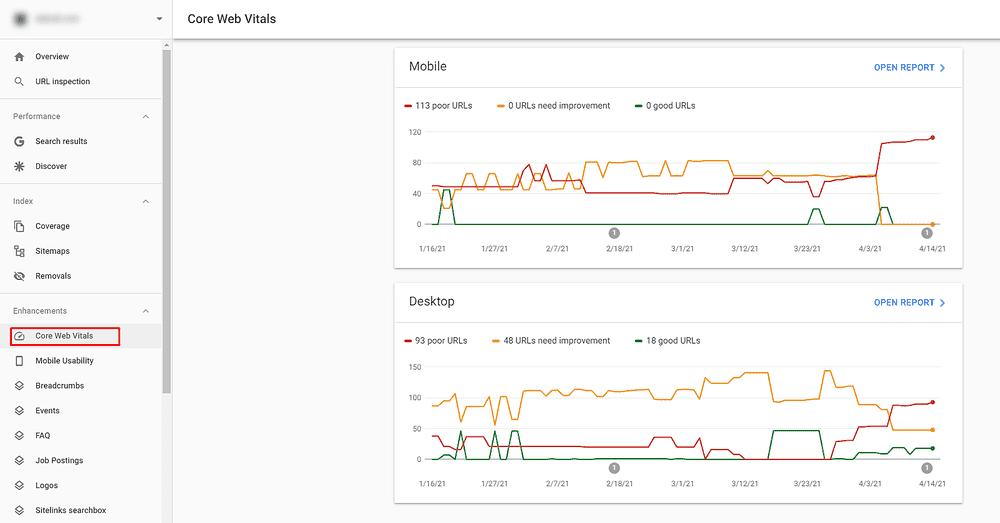
After an announcement made in May 2020 that Google will roll out a new core algorithm update this year in May that will concern the Core Web VItals, it was clear that how the user experiences the site will be of enormous importance. And the Core Web Vitals Section will give you insights into this matter.
You can notice how the data gathered is broken down by mobile and desktop. Three very important segments are included in the report, and they are
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Improving these three segments will be vital for your site’s rankings after the Google Update in May 2021 is completed. If there are URLs listed as Poor in the report, make sure you handle them first. Once you fix the issue, resubmit it in the GSC to see whether Google will accept the fix.
Mobile Usability
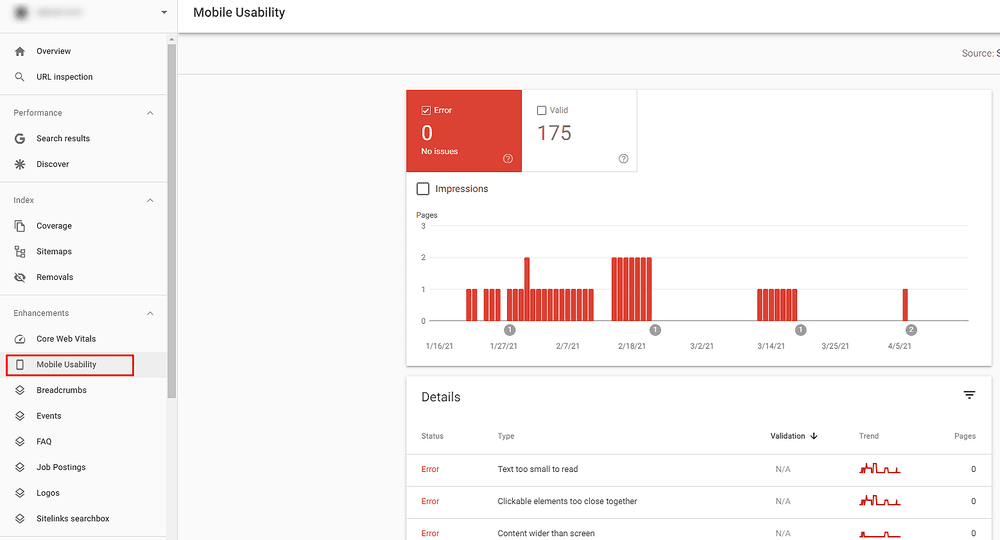
This report helps you find issues with design and development with the mobile version of the site. You might think that you have the best design, but if it is not developed the right way to be mobile-responsive, it will provide a catastrophic user experience for the site’s visitors. The Google Search report might show you the following issues:
- Content wider than the screen
- Clickable elements too close together
- Viewport not set
- Text too small to real
Breadcrumbs
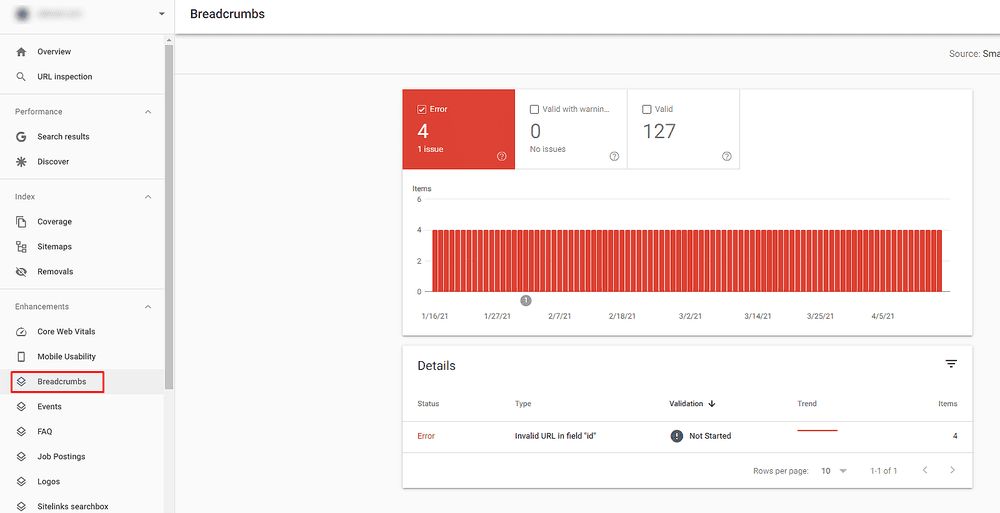
The Breadcrumbs report shows you which issues that may be preventing breadcrumbs from displaying in the SERPs need to be fixed. Also, you can check whether your structured data show in the SERPs. It will tell you which URL you need to check, and you will need to analyze each error individually. Even though structured data is not a ranking factor, they still affect the user experience on the websites, which is a ranking factor.
Events, FAQ, Job Postings, Logos, Sitelinks Searchbox
These are the rest of the reports in the Enhancement section. They give insights about the rich results you have ranking on SERPs and whether any critical issues need fixing.
To Sum Up
This Google Webmaster tutorial should give you an insight into how to start using the Google Search console, especially if you are an SEO beginner. It can help you perform the SEO audit of website and start fixing the errors that prevent you from getting high-ranking positions on Google.